Economic analysts and observers suggest that China is likely to deviate from its national GDP target amid the COVID-19 pandemic. Moreover, policymakers are continuously urged to prioritize employment and business support. Thus, different measures should direct toward eliminating poverty and preventing closure of the business economy.
Have a look at our previous article about Company Closure: A Guide for Foreign Businesses in China
The Chinese Communist Party’s hundredth anniversary marked China’s goal of achieving a double economic growth in the span of five years. Keep reading to learn more.
China’s national GDP target by 2020
Based on the World Bank metrics, China’s national GDP has decreased over the years from 2010 until 2018. Last year, it settled with an annual GDP rate of 6. 1 percent.
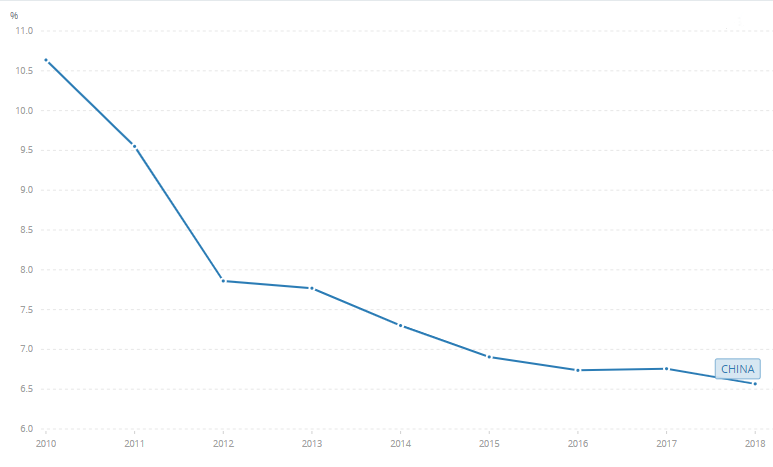
Source: The World Bank
The first quarter of 2020 has proven to be challenging as shown by the country’s first GDP contraction by 6.8 percent since 1992. This was the initial impact of the COVID-19 outbreak felt from January to March period.
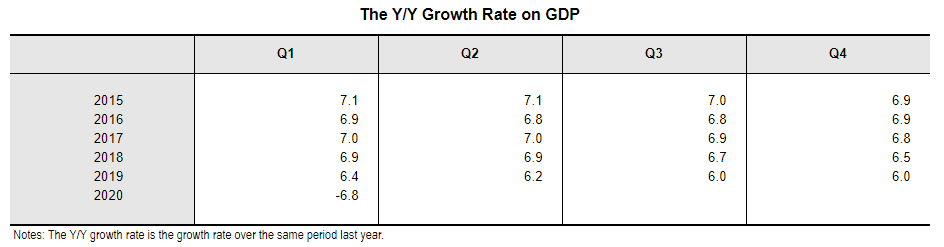 Source: National Bureau of Statistics of China
Source: National Bureau of Statistics of China
According to the International Monetary Fund 2020 economic outlook, China’s real GDP is projected to grow only by 1.2 percent. However, it has forecast an expansion of China’s economy by 9.2 percent in 2021.
The graph below represents China’s growth rate change year-on-year from 2011 to 2021.
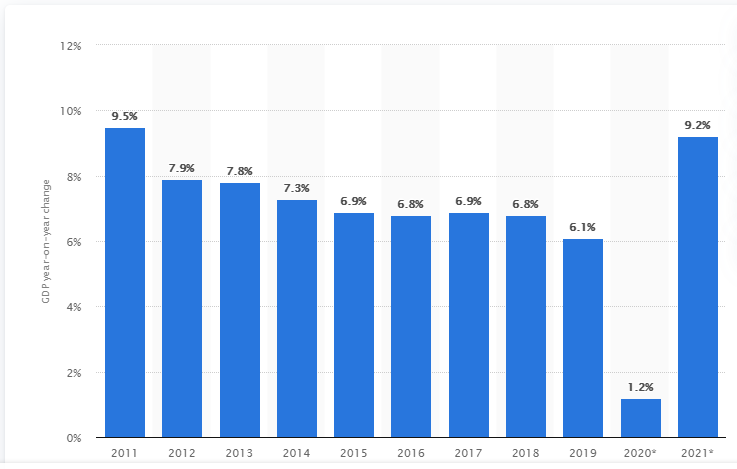
Source: Statista Research Department, Gross Domestic Product China
Exports, comprising about 18 percent of China’s national GDP are presumed to fall by the first quarter. Meanwhile, industrial profits are also expected to reduce by 25 percent. Data from the National Bureau of Statistics show that industrial profits decreased by 34.9 percent year-on-year in March.
Impact on China’s domestic economy: looking at the numbers
According to the NBS report on China’s national economy, the government’s coordinated efforts have enabled the gradual restoration of the country’economic production and people’s living. We look at the overall report presented by the bureau for the first two months of the year.
1. Overall agricultural production
Until the end of February, wheat production in winter increased by 3 percentage points compared to the last year of the same period. The report further highlighted the increase in vegetable cultivation and guaranteed supply of agricultural materials such as seeds, chemical fertilizers, and pesticides.
China state-media Xinhua also reported that China’s agriculture sector remains robust despite the impact of COVID-19. It noted a 35 percent year-on-year (YoY) increase in the added value of the planting industry in the first quarter of 2020. Furthermore, the breeding sow stock also expanded by 9.8 percent since the end of 2019.
2. Industrial and goods production
The statistics bureau noted a drop by 13.5 percent (YoY) on the total added value of the industrial enterprises above the designated size in the first two months of 2020.
There is a notable decrease in the total added value of foreign enterprises by 21.4 percent (YoY) and private enterprises by 20. 2 percent (YoY). Moreover, the manufacturing sector manifested the highest decline by 17.7 percent (YoY), followed by mining and electricity, thermal power, gas and water production, and supply.
On the other hand, medical, high tech and food products such as frozen meat and instant noodles showed significant growth.
3. Services production and emerging service industry
Financial services, information technology, and telecommunication recorded growth both in service production and business activity.
4. Sales of physical goods
Total retail sales of consumer goods declined by 20.5 percent (YoY), amounting to RMB 5,213 billion. Thus, income by consumption from catering and sales of retail goods experienced a considerable blow in the first two months.
5. Investment in fixed assets and investment in high tech and social sectors
Investments in fixed assets concerning infrastructure, manufacturing, real estate development, and high-tech industries declined. On the other hand, investment in inspection, testing, and professional technical services increased.
6. Market and consumer prices
The consumer price index (CPI) of commodities generally went up by 5.3 percent (YoY) which include the following:
- Food (grains, pork, fresh vegetables, except fruits);
- Tobacco and alcohol;
- Clothing and housing;
- Daily necessities;
- Transport and communication;
- Education, culture, and recreation;
- Medical services and healthcare, and others.
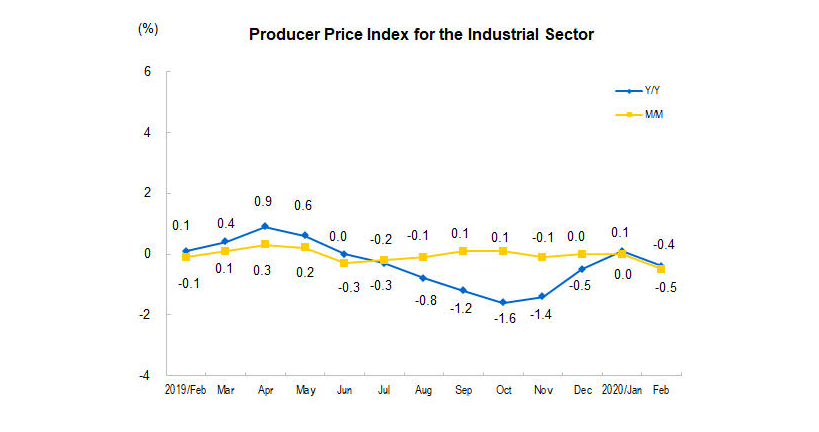
Among the food commodities, the prices of fresh fruits went down by 5.3 percent. Furthermore, the producer price index (PPI) for the industrial sector also dropped by 0.4 percent (YoY) in February.
Source: National Bureau of Statistics of China
7. Employment rate
The statistics bureau reported increased employment in urban areas by 1.08 million employed people during the first two months of the year. On the other hand, the department surveyed an unemployment rate of 5.06 percent among individuals aged 25 to 29. Meanwhile, employment among younger people aged 20 to 24 decreased by 0.6 percentage points higher than the former. The authority noted, however, that the rates of unemployment lowered in February compared to January.
8. Export and import deficit and trade structure optimization
In January and February, China experienced a decrease in the total value of its imports and exports by 9.6 percent (YoY). This amounted to RMB 4,123.8 billion where exports covered RMB 2,040.6 billion and imports equaled RMB 2,083.2 billion. The trade balance amounted to RMB 42.6 billion deficit.
Despite that, the bureau indicated that the value of general trade was 0.3 percentage higher than the same period of last year. Based on this, the total value of exports and imports accounted for 60.6 percent.Positive changes in April 2020
On May 15, 2020, the statistics bureau released an updated April report showing some notable changes in China’s recent national economic performance.
According to the report, the industrial production of enterprises above designated size and the manufacturing sector grew by 3.9 percent and 5.0 percent, respectively. Moreover, although the consumer price continued to go up, it recorded a slower decline compared to March.
However, the number of unemployed people rose to 3.54 million in total from January to March. The unemployment rate among individuals aged 25 to 29 consisting of the major labor force reached 13.8 percent, higher than the previous first two months. Furthermore, the urban unemployment rate in 31 major cities was 5.8 percent, 0.1 percentage point higher than in March.
The total value of imported and exported goods continues to decline, albeit, slower than previously recorded.
What to expect from China’s national GDP recovery?
As China’s focus on steady recovery seen, economic experts expect more policy measures directed at fighting poverty and uplifting employment. In view of the current situation, many economists agree on a more realistic approach to stabilize jobs and secure people’s livelihoods.
On the other hand, if China will have to continue reaching its double growth target this year, the country must achieve a GDP growth of around 5.5 percent, according to estimates. However, it may be hardly attainable due to the continuous challenge brought about by the COVID-19 pandemic. The interruptions in the Chinese, as well as the global economies, would prove to affect economic growth in the long run.
The median forecast for China’s domestic GDP growth rate in the worst scenario reflects a decline of 5 percent, following the country’s first recorded contraction since the 90s.
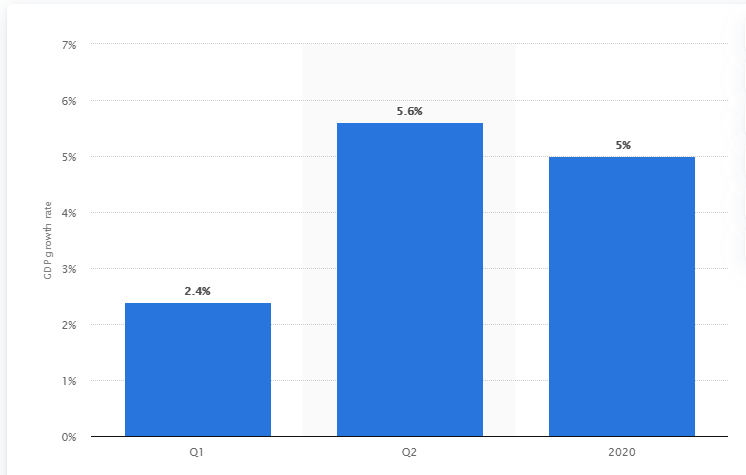
Source: Statista Research Department
Following the call to abandon the country’s double sizing of its economy, the Chinese government will be forced to focus its recovery on fiscal measures supporting jobs and businesses. But further clarifications will surface as soon as the upcoming National People’s Congress “work report” is held this May 2020.If you want to know more about doing business in China, contact our team for consultation and assistance. Follow us on social media to get the latest news!
Our experienced team has the necessary expertise and the know-how to support you with your business – have a look at the services we offer.
See how much salary you receive after tax and check your company value without leaving WeChat!
Also, our Mini Program can estimate the salary in your industry, for your experience level and position. A huge help for salary negotiations!