The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic is bound to affect the economic trade and businesses around the world. As it expands in more than 100 countries, a significant impact on the flow of trade and economy is looming. To note, China and the United States have just come into terms with a trade deal in early January to combat the global effect of the trade war.
Read our latest post about the Trade Deal between U.S. and China: Taking the First Step
Looking back on where it all started, China is still recovering from the cost of the virus spread on its economy. What is the overall impact of the COVID-19 outbreak on China’s domestic economy? Does the pandemic pose a great economic risk as well? Read to gain some useful insights.
Impact on foreign trade in China
For two months since the outbreak of COVID-19 in China, China’s foreign trade showed a significant downward trend. From January to February, there was a sharp decline in China’s total export and import value of traded goods as shown below.
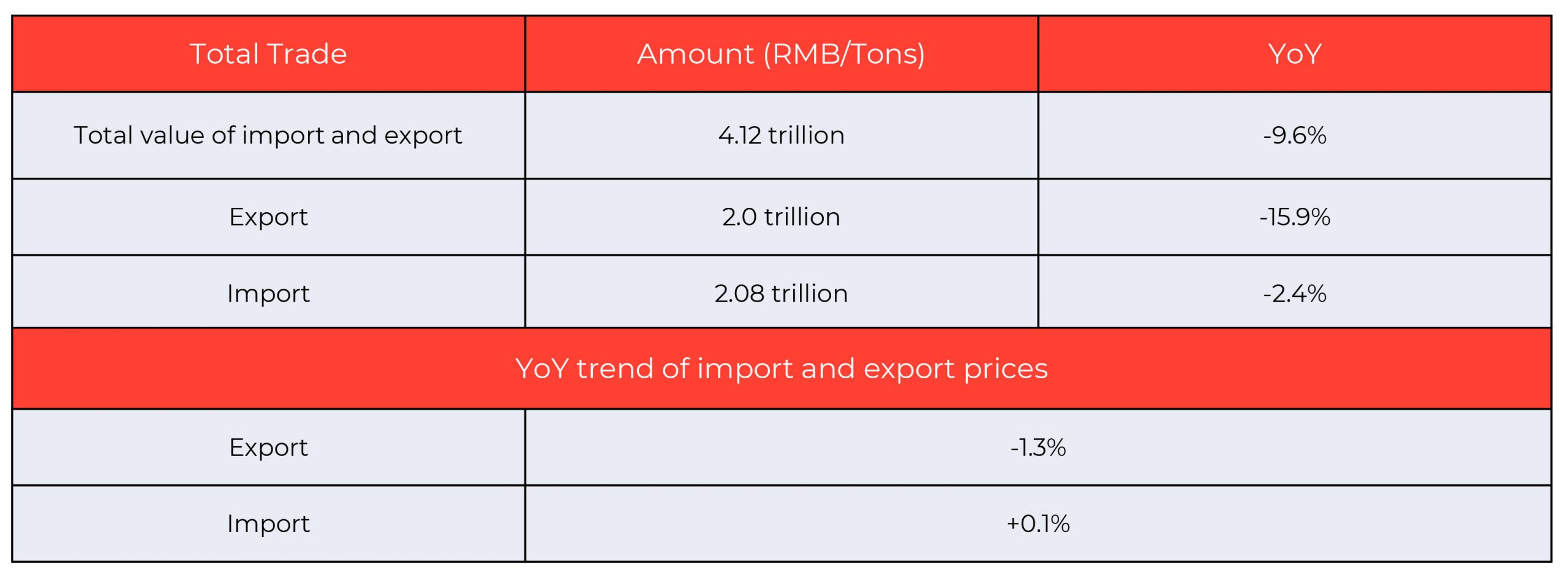
Below shows the volume of export and import for January and February, amounting to the total volume of freight transport.

Source: China Business Intelligence Network
*Year-over-year (YoY) is a method of comparison used to gauge the financial performance on an annual basis. It is often used to analyze growth patterns and trends.
During the epidemic situation in China, imports and exports to the U.S., the E.U., and Japan generally declined. For instance, the total value of traded commodities between China and the U.S. has declined to 19.6 percent year-over-year. Chinese exports to the U.S. in January and February also fell by 26.5 percent YoY, amounting to RMB300.1 billion.
On the other hand, imports and exports to ASEAN grew by 2 percent, amounting to RMB594.11 billion. ASEAN, therefore, became China’s largest trading partner amid the COVID-19 outbreak in the country. Among the 23 major countries that China exports from, only the Philippines, Taiwan and Vietnam saw positive growth in their total export value.
China’s overall imports from five major countries including South Korea, Taiwan, Japan, Australia, and the U.S. showed a negative trend in January 2020. Moreover, imports from Canada also fell to 42.3 percent YoY. China also experienced a drop in imports from South Africa, France, and Hong Kong by more than 20 percent.
Impact on the profits of large-scale industrial enterprises in China
China’s Statistics Bureau recorded a YoY decline in the profits of industrial enterprises by 38.3 percent from January to February. Foreign, Hong Kong, Macao, and Taiwan invested enterprises showed the lowest points at 53.6 percent YoY trend.
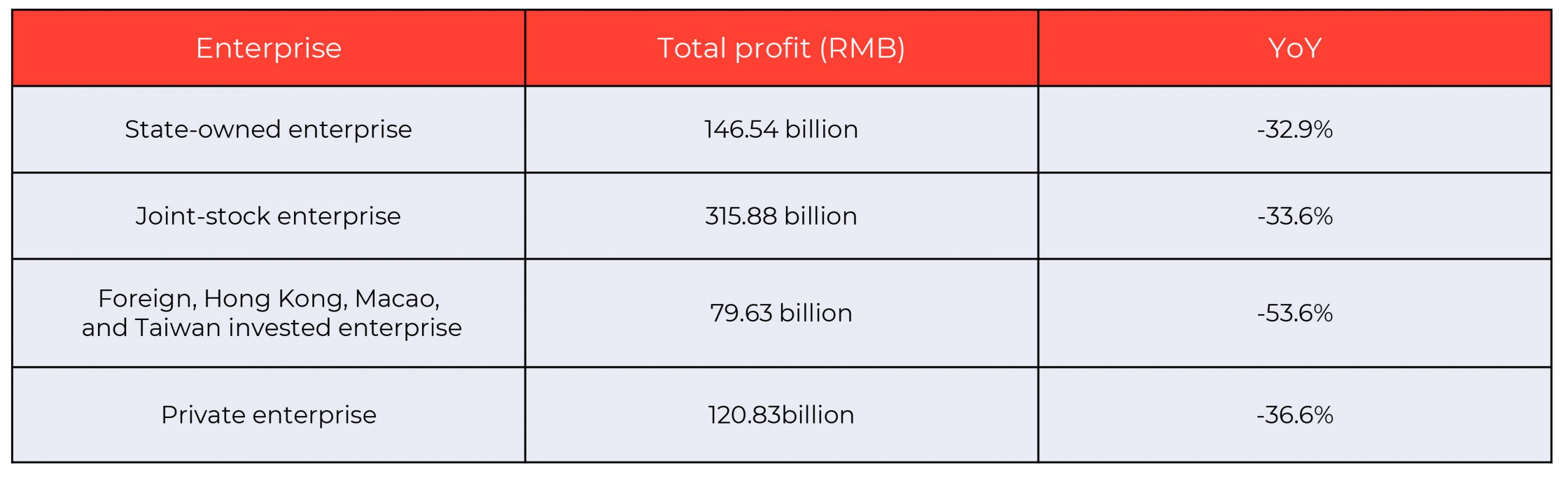
Source: China Federation of Logistics and Purchasing
The table below shows the changes from January to February in the relevant data of the profit statement of industrial enterprises above designated size.
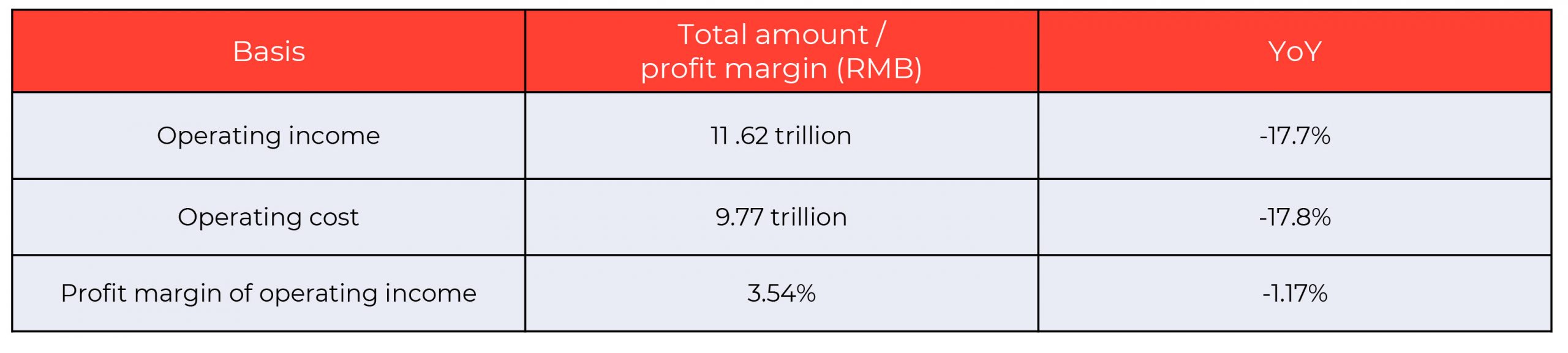
Source: China Federation of Logistics and Purchasing
*Enterprises above designated size refers to the annual business revenue of industrial enterprises amounting to RMB20 million or more.
The worldwide financial stress makes it difficult to estimate the effects on the revenue. However, the decrease in operating cost appears to have reached a bottleneck.
The table below shows the changes in the relevant data of the balance sheet data of industrial enterprises above designated size by the end of February 2020.
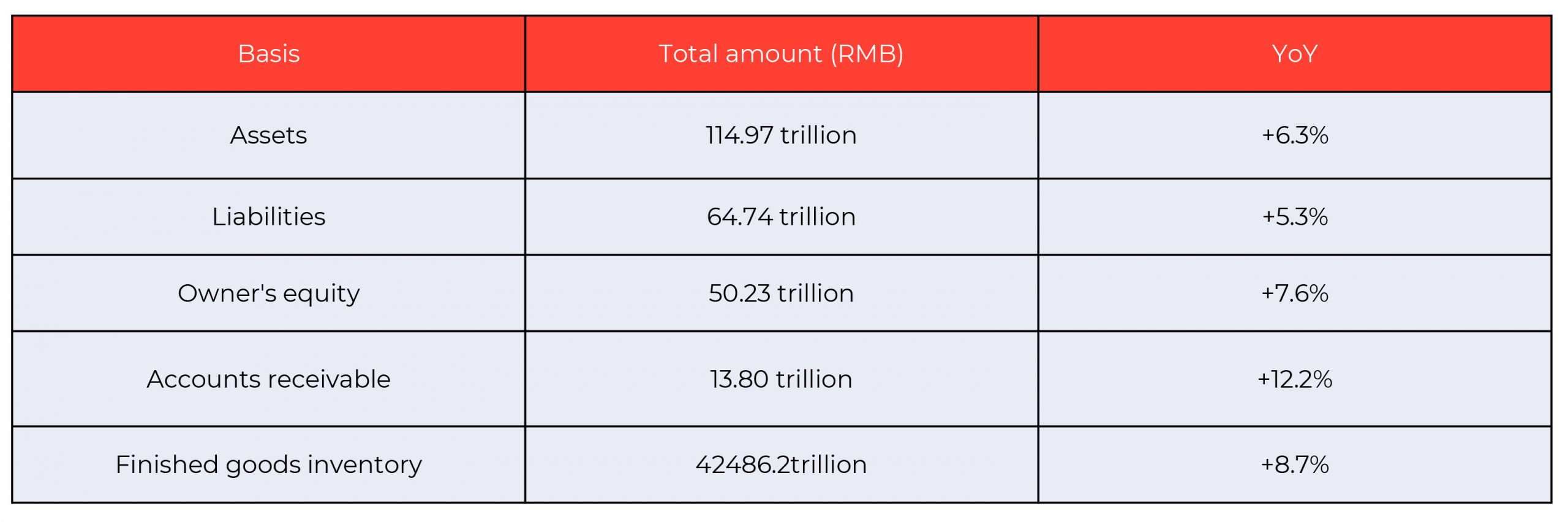
Source: China Federation of Logistics and Purchasing
The asset/liability ratio is calculated at 56.3 percent by the end of February, a YoY decrease of 0.6 percentage points.
This decrease, however, only reflects the initial stage of the COVID-19 impact on China. After this period, investors will become more conservative for scale expansion. Therefore, the capital source for the increase of fixed assets will become uncertain.
The speed for the increase of investment may be slowed down, which will drive the further decrease of asset/liability ratio.
Key problems in the industrial and supply chain
- Bulk commodities increased by 0.8 percentage points in February.
- China’s inventory index for commodity turnovers decreased from 25.0 percent to 24.5 percent.
- Some enterprises had great difficulty in production and operation due to a shortage of raw fuel.
- Disruption in international shipping led to transport delays of export containers, thus affecting the manufacturing and related industries.
Ongoing impact on China’s trade
Nearly all traditional B2B trade shows in China were canceled due to the COVID-19 outbreak. But on the other hand, the spread of COVID-19 in North America prompted the region to increase purchases of protective equipment from China. Regardless of that, China still faces challenges in trade due to recent restrictive measures imposed against foreign countries. For example, the reduction of international or long-distance flights does slow down globalized trading. Furthermore, Chinese authorities have extended the clearance time and inspection for the entry of goods. This could, therefore, lead to a shortage of goods and delays in replenishment.
Lastly, despite the resumption of production by China’s foreign trade enterprises, there is a continuous challenge in normalizing the global supply chain. This is because the pandemic forces different countries to impose strict travel measures, and thus, affecting the flow of trade.
Risk on China’s semiconductor industry
Huge semiconductor companies, as well as nearly 100 SMEs, had stopped their production and operation during the virus outbreak. This includes Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix, two of the biggest semiconductor companies in South Korea. At the same time, modern enterprises and factories in China were forced to shut down due to a shortage of semiconductor supplies. Japanese enterprises also occupy a major section of high-end manufacturing fields such as semiconductors. For these reasons, China’s semiconductor trade with Japan and South Korea has been affected.
As Japan and South Korea are currently facing the threat of the COVID-19 pandemic, their global semiconductor production may also be seen at risk. Thus, it could further generate a relative impact on China’s semiconductor trade.
The Statista Research Department predicted a steep decline in the global revenue for the semiconductor industry due to the pandemic, adding that global economic disruption would continue for a year. This effect is expected to bring serious implications for the wider technology industry.
The 2020 China Outlook report on the semiconductor industry revealed that China accounted for 50 percent of the global semiconductor consumption in 2019. Therefore, the persistence of the pandemic can possibly impact China’s electronic trade.
Conclusion
For the most part, people’s spending habits and lifestyles can dictate the direction of the impact of the pandemic on the Chinese economy. There is no doubt that the consequence of lockdowns may have altered consumers’ psychology and behavior toward spending.
Nevertheless, the latest survey on the Chinese consumer behavior post-COVID-19 showed cautious optimism. This could suggest a regained confidence among Chinese consumers. The report also indicated that the Chinese are also slightly optimistic about the economy after the end of the outbreak. Results revealed that consumers are optimistic that the Chinese economy will rebound in two to three months.
According to China International Capital Corporation Limited (CICC) research, China’s economic growth will slow down by 2.8 percent YoY in 2020, before rebounding to 11.1 percent YoY in 2021. Beyond this, however, there is a promising surge in investment for the healthcare sector as China pours more capital on the management and development of public health. Thus, private sectors in the healthcare industry can take advantage of growing opportunities brought by the pandemic.If you want to know more about doing business in China, contact our team for consultation and assistance. Follow us on social media to get the latest news!
Our experienced team has the necessary expertise and the know-how to support you with your business – have a look at the services we offer.
See how much salary you receive after tax and check your company value without leaving WeChat!
Also, our Mini Program can estimate the salary in your industry, for your experience level and position. A huge help for salary negotiations!