A sole proprietorship or self-employed business is a common company set up for small traders in China. Opening a small enterprise is a great way to establish a market presence in China and take advantage of several business opportunities.
Read our previous article about The Startup Business Environment in China
Like any business, however, a sole proprietor or self-employed business owner must register in accordance with China’s laws and regulations. Foreigners may wish to own a business directly as a sole proprietor. But is it permitted in China? Keep reading to find out!
What is a sole proprietorship or self-employed business?
A sole proprietorship as its name implies refers to individual ownership. Becoming a sole proprietor or sole trader means that only a single individual runs the company. Thus, all revenues and liabilities are carried out by the individual owner. A sole proprietorship has unlimited liabilities and cannot have shareholders. Thus, a sole proprietor keeps all profits and bears all related income taxes.
A sole proprietor or self-employed business owner is typical of a restaurant or a shop owner. Some suitable businesses include offline retail stores, coffee shops, bars, gyms, grocery stores, flower shops, sales counter of products, etc.
Can foreigners own a self-employed business?
According to Article 3 of the law on sole proprietorship, a sole proprietorship enterprise’s main place of business shall be its domicile. This means that without a domicile status in China, a foreigner cannot be a sole trader. Nevertheless, it is possible to invest in a small enterprise as such by setting up a Joint Venture (JV) that requires a Chinese partner or applying directly for a Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprise (WFOE).
Check out An Investor’s Guide to Incorporating WFOEs in China
Establishing a sole proprietorship has a lower set up, taxation, and maintenance cost. However, the individual business owner’s personal assets are not separate from the company’s assets. Therefore, the owner is responsible for paying off all debts using his or her personal property in case the company’s funds become insufficient.
What are the conditions for setting up a sole proprietorship?
- The investor is a natural person;
- It has a legal enterprise name;
- The enterprise has registered capital contributions by the investor;
- It has a fixed production and operation site and necessary production and business conditions;
- The enterprise has the requisite employees.
Documents required
- An application form for the establishment of a sole proprietorship enterprise signed by the investor ;
- The investor’s identity certificate;
- Proof of the domicile of the enterprise;
- Other documents required by the State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR).
The individual-owned enterprises must register within 15 days from the determination of the following information below.
- Name and domicile of the enterprise
- Name and residence of the investor
- Amount and method of capital contribution of the investor
- Business scope
Applicants must submit the relevant documents to the SAMR and obtain an official business license and company a seal upon approval.
Should sole traders or self-employed business owners pay for corporate income tax?
In 2000, China’s State Council through State Development (2000) No. 16 decided to eliminate the payment of corporate income taxes for sole proprietors or individual-invested enterprises. Instead, taxes on the production and operation of sole enterprises are levied on their individual income taxes.
Check out Foreign Income Tax Policy for Resident Taxpayers in China
What are the legal liabilities of a sole proprietorship?
The following are the violations and corresponding fines imposed on individually-owned enterprises.
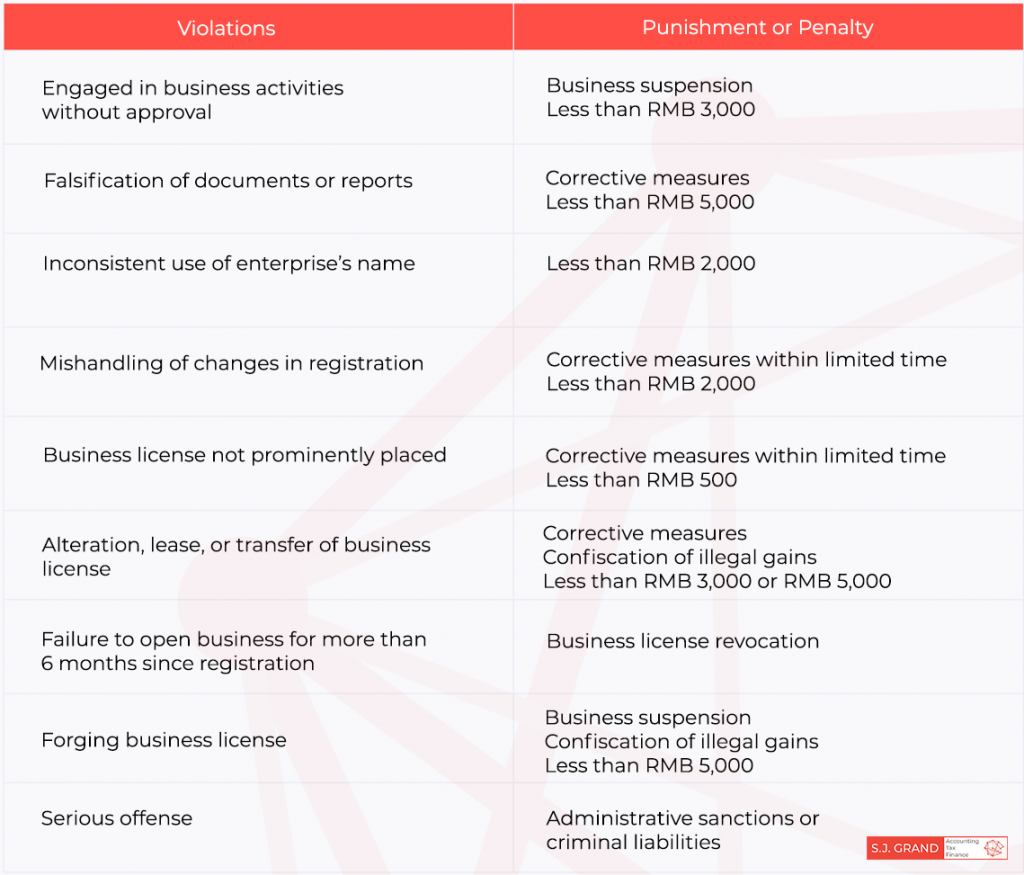
It is possible that the registered owner may entrust the management of the sole proprietorship to another person or employee. However, he or she should make a written contract of entrustment, citing the scope of conferred rights. Furthermore, individual business owners who decide to hire employees must provide employment contracts following the law. The authorities also oblige the owners to contribute to social insurance payments and set up accounting books for auditing purposes.
If the owner decides to liquidate the company, he or she can either do it or creditors can apply to the People’s Court to appoint a liquidator. On the other hand, if creditors fail to notify the owner of the payment of debts within five days after dissolution, the liability for debt will be cleared.
Conclusion
China’s law on sole proprietorship does not apply to foreign sole enterprises. Hence, foreigners cannot register as sole traders or self-employed business owners. However, there are other options as mentioned such as setting up a WFOE or JV. The former, however, requires someone to have a better understanding of doing business in China while the latter may need a partnership with a local to start a business. Take note that in the JV structure, the Chinese partner is the sole shareholder of the company, hence, a foreign investor will have no legal ownership rights.
Contact us
If you want to know more about doing business in China and need assistance with setting up a company in China, contact us to avail of our specialist services or visit our company registration page. Moreover, you can take advantage of Kwikdroid, our easy-to-use, 24-hour access company management tool for any type or size of business.
Kwikdroid is a Cloud-based accounting and company solution that will be made available in your workplace in no time.
S.J. Grand also offers Cloud ERP services for your business if you are currently experiencing difficulty in managing your operations amid the COVID-19 pandemic. Check out our IT services page for more details.






