All companies in China have to pay value-added tax (VAT) based on their taxable revenue. According to related taxation laws of China, VAT payers are categorized into general taxpayers and small-scale taxpayers based on their annual taxable sales.
Taxpayers with annual revenue exceeding the ceiling set for small-scale taxpayers must apply for general taxpayer status. The current ceiling for all companies is RMB 5 million a year.
Have a look at our previous article on VAT Exemption on Sales of Services to Foreign Countries
Having a general taxpayer status provides the opportunity to apply for export VAT refunds and credit input VAT from output VAT.
Determining small-scale and general VAT payers
Small-scale taxpayers
The standard for small-scale VAT payers is that the annual VAT taxable revenue is RMB 5 million yuan or less. Thus, small-scale taxpayers are those engaged in the production of goods or provision of taxable labor services, and whose annual sale amount subject to VAT is RMB 5 million or less. Moreover, small-scale taxpayers engaged in wholesale or retail of goods have annual taxable sales of RMB 8 million or less.
Application criteria:
- An enterprise shall be ratified as a VAT small-scale taxpayer upon registration with no need for a separate application.
- The company’s annual taxable sales shall not exceed RMB 5 million.
VAT rate:
The applicable levy rate is 3 percent.
Way of collection:
VAT and its surcharges shall be declared on a quarterly basis.
General taxpayers
Taxpayers who do not fall under small-scale taxpayers are general taxpayers. Further, general taxpayers have different VAT rates for specific industries
Application criteria:
- An enterprise shall apply for the qualification of VAT general taxpayers when its annual taxable sales reach or exceed RMB 5 million, if it doesn’t apply, it shall be compulsorily ratified as general VAT payers.
- A newly registered company or company with annual taxable sales not exceeding RMB 5 million can apply for the qualification of the general taxpayer if it has had a proper accounting system and is able to provide accurate tax information to in-charge tax authorities.
The VAT rate for applicable industries:
13%
Sales/ Imported goods
- Labor services
- Tangible personal property leasing services
9%
Sales/ Imported goods (Special items)
- Food and other agricultural products, edible vegetable oil, and edible salt
- Tap water, heating, air conditioning, hot water, gas, liquefied petroleum gas, natural gas, dimethyl ether, biogas, coal products for residential use
- Books, newspapers, magazines, audio-visual products, electronic publications
- Feed, fertilizer, pesticide, agricultural machinery, agricultural film
- Other goods specified by the state council
- Transportation, Postal, Basic Telecommunications Services, Construction, Real estate Leasing Services, Transfer of Land use right, and Sale of Real Property
6%
- Modern services, such as financial or value-added telecommunications services
- IT and Cultural Creative Services, and other life services
Way of collection:
VAT and its surcharges shall be declared on a monthly basis.
Pros and cons of switching to VAT payer status
There are considerations when determining whether to be a general taxpayer or a small taxpayer. This mainly concerns tax cuts or exemption policies associated with the taxpayer status.
Small-scale taxpayers with monthly sales of less than RMB 100,000 and quarterly sales of less than RMB 300,000 are exempt from paying VAT. On the other hand, from April 2019 to December 2021, general taxpayers engaged in production or livelihood service can enjoy a 10 percent additional input VAT deduction or super deduction to offset their VAT payable. To qualify, general taxpayers must meet beyond 50 percent of their total sales revenue from main businesses.
Below are the different main businesses that can qualify for the super deduction:
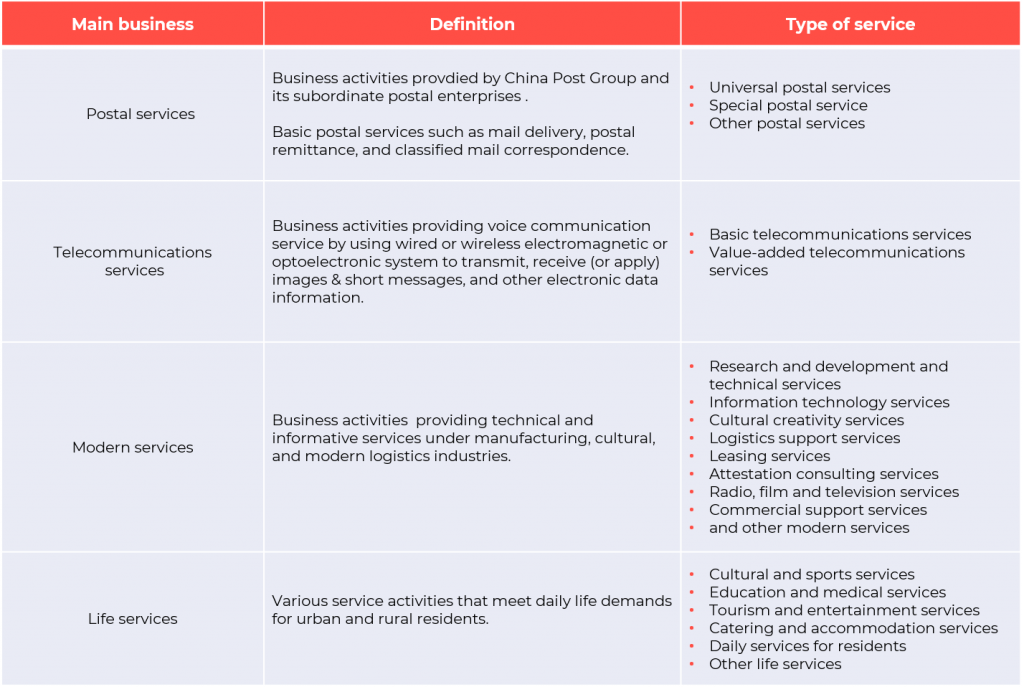
General taxpayers can qualify for a refund of unused input VAT since April 2019, given that they meet certain conditions. Furthermore, there are several VAT preferential policies intended for certain industries and business activities. Thus, enterprises must consider these factors before deciding to be a general taxpayer or not.
Input VAT
An input VAT is the amount of VAT paid by the general taxpayer on the purchase of goods and taxable services.
Small-scale taxpayers
Small-scale taxpayers cannot deduct input VAT credit from the output VAT taxable amount. They cannot issue VAT special invoices and instead, can only use ordinary invoices purchased from the tax bureau. However, since August 2016, China has piloted a program allowing small-scale taxpayers to issue special VAT invoices by themselves. The following industries belong to this program so far:
- Hotel industry
- Authentication and consulting
- Industrial, information transmission, software and IT
- Leasing and business service
- Scientific research and technical services
- Residential service, repair, and other service industries.
Small-scale taxpayers who had switched their status from general taxpayers can also continue to issue special VAT invoices by themselves. This is applicable only if the approval for the special VAT invoices happened before the switching date.
General taxpayers
For general taxpayers, on the other hand, the input VAT is deductible from the output VAT. They can deduct the input VAT as shown on the VAT special invoice for purchasing goods, assets, and taxable services. Furthermore, input VAT is also deductible on the withholding VAT incurred for sending payments to foreign companies.
Have you read? VAT Exemption on Sales of Services to Foreign Countries
Enterprises must undergo certain procedures for applying to change from small-scale taxpayers to general taxpayers. Moreover, the compliance cost for general taxpayers is higher than that of small-scale taxpayers.
Enterprises having clients that mostly ask to issue general scale VAT invoices should have no choice but to apply for a general taxpayer status. Moreover, enterprises engaged in production and export may better apply as general taxpayers to take advantage of the “Exemption, Credit and Refund” policy.
It is advisable to maintain a small-scale taxpayer status if an enterprise only conducts some after-sale or market activities and most of its service income comes from overseas headquarters. Where most of the cost derives from labor cost or rental, there is not much input VAT to be credited as labor cost, for example, cannot incur input VAT based on the current VAT regulations.
Types of tax invoices for VAT payers
There are two types of invoices that taxpayers can issue: special VAT invoices (fapiao) and general or ordinary invoices. Below are the conditions regarding the issuance of these invoices.

Meanwhile, the following transactions are not allowed to use special VAT invoice:
- Goods and taxable services supplied by small taxpayers;
- Selling of VAT-exempt goods;
- Selling of goods or taxable services to the consumer;
- Sale of specific types of goods at the retail sector
- (such as cigarette, wines, food, clothing, shoes, hats, and
cosmetics products); - Sale of export goods or taxable services for
consumption outside the PRC; - Using goods for non-taxable items (such as using
stock-in-trade for the construction of own assets); - Using goods for collective or personal consumption;
- Supplying goods at no consideration (a gift);
- Provision of non-taxable services (except for those
subject to VAT in mix sales).
Current VAT rates in China

Contact us
S.J. Grand’s tax and accountancy services provide advisory on China’s tax and business regulatory environment as well as assistance in optimizing your direct or indirect taxes for the benefit of your business. Our tax experts can also guide you through the process of changing your VAT payer status. Contact us to get you started.
If you are interested to learn about our latest Cloud-based company solution, contact us, or go to our Kwikdroid page to check the prices and packages we offer, no matter the size or type of company.







